The Big Lie About Nuclear Waste - What if we could actually USE nuclear waste
Last updated: May 28, 2023
The video discusses the potential of using nuclear waste as a clean energy resource and how it could have been a major source of energy for the future, but the technology was left behind due to concerns about nuclear waste.
The video discusses the potential of using nuclear waste as a source of clean energy. It highlights a nuclear reactor developed by Argonne National Laboratory in the 1960s that could generate electricity from nuclear waste.
The video also explores the concerns and fears associated with nuclear waste and nuclear energy, as well as the potential benefits of reusing nuclear waste as a clean energy resource. The main obstacles to implementing this technology are cost and global politics, rather than fundamental technological limitations.
The video concludes by discussing the efforts of individuals and companies working to bring this technology back and create a cleaner energy future.
- A nuclear reactor was developed in the 1960s that could make electricity out of nuclear waste.
- Nuclear waste is an incredible clean energy resource that is just sitting there.
- Our nuclear waste isn't radioactive trash, it's a clean energy resource.
- There is enough used fuel in the US alone to generate power for the country for the next 150 years.
- Nuclear waste recycling is a promising technology that could make nuclear power more sustainable.
- Nuclear power is a low-carbon energy source that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nuclear power can help meet the growing demand for energy in developing countries.
The Big Lie About Nuclear Waste - What if we could actually USE nuclear waste? - YouTube

The Potential of Nuclear Waste
- A nuclear reactor was developed in the 1960s that could make electricity out of nuclear waste.
- This reactor was different from the nuclear power plants that supply homes with electricity today.
- Nuclear waste is an incredible clean energy resource that is just sitting there.
- Technology was left behind due to concerns about nuclear waste.
- Our nuclear waste isn't radioactive trash, it's a clean energy resource.

The Clean Energy Future We Could Have Had
- In the 1960s, it was predicted that we would use nuclear waste to build a clean energy future by the year 2000.
- Today, we are nowhere close to that.
- Our nuclear waste could have been a major source of energy for the future.
- We left behind a technology that could change our energy future.
- People are trying to bring that future back.

Concerns About Nuclear Energy
- There are concerns about emissions and abundant power.
- We need clean energy to energize the city.
- New nuclear reactors are being developed to guarantee a plentiful supply of atomic power for the nation and the world for centuries to come.
- People are afraid of nuclear energy.
- Events and things freak us all out.

The Big Lie About Nuclear Waste - What if we could actually USE nuclear waste? - YouTube
The Potential of Reusing Nuclear Waste
- There is enough used fuel in the US alone to generate power for the country for the next 150 years.
- The technology is there to reuse nuclear waste as a large energy source.
- If nuclear waste is reused more than once, it can dramatically cut down on the amount of time that the waste is radioactive for.
- The problems are cost and global politics, not fundamental technology.
- Nuclear waste is not just a problem, it's a potential solution.

What is Nuclear Waste?
- Nuclear waste is a byproduct of nuclear power generation.
- It is a mix of uranium-238, uranium-235, and unstable atoms that give off ionizing radiation.
- Ionizing radiation can be harmful to human tissues and DNA.
- Nuclear waste remains radioactive for hundreds of thousands of years.
- Most nuclear waste in the US is stored in dry casks at nuclear power plants.

The Once-Through Fuel Cycle
- The US currently uses a once-through fuel cycle for nuclear power generation.
- Uranium is taken out of the ground, used once, and then stored as nuclear waste.
- This is a wasteful and inefficient process.
- Most of the uranium in natural uranium is not useful for nuclear power generation.
- The key is to figure out how to filter out the useful uranium from the waste.

Nuclear Waste Recycling
- Nuclear waste recycling is a process that can extract useful uranium from nuclear waste.
- The extracted uranium can be used as fuel for nuclear power generation.
- This process can reduce the amount of nuclear waste that needs to be stored.
- Argonne National Laboratory is one of the places that is testing nuclear waste recycling in the US.
- Nuclear waste recycling is a promising technology that could make nuclear power more sustainable.

The Potential of Nuclear Waste
- Nuclear waste has the potential to be a major source of clean energy.
- Nuclear waste recycling could make nuclear power more sustainable and reduce the amount of nuclear waste that needs to be stored.
- Nuclear power is a low-carbon energy source that can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nuclear power can provide a reliable source of energy that is not dependent on weather conditions.
- Nuclear power can help meet the growing demand for energy in developing countries.
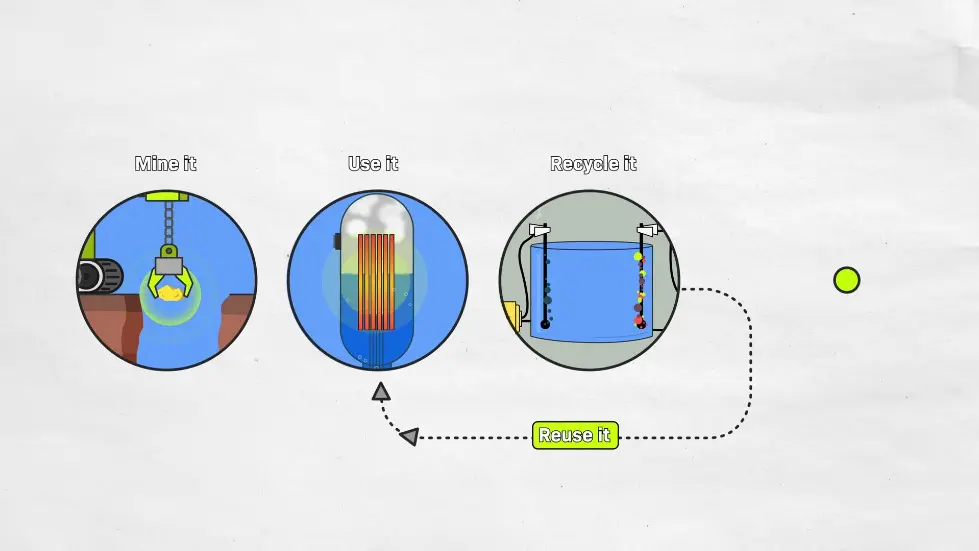
Using Nuclear Waste as a Clean Energy Resource
- Nuclear waste has been a major block to the use and improvement of nuclear power.
- Technology exists to use nuclear waste as a clean energy resource.
- Nuclear waste can be cut up into little pieces and dissolved into a vat of molten salts.
- Electricity is run through the vat to separate the uranium and other useful materials from the rest of the waste.
- New fuel rods can be made out of the deposits of useful materials and put back into a reactor.
- This process can be repeated multiple times, reducing the radioactivity of the waste and making it easier to store.

The Ban on Nuclear Recycling in the United States
- In 1977, President Jimmy Carter announced new policies to stop the growing risk of nuclear war, including stopping all nuclear recycling.
- The ban on nuclear recycling was lifted by President Reagan in 1981, but by then, companies had invested in reactors that couldn't recycle.
- The main claim against nuclear fuel recycling is that it is too high cost and not economical compared to using new uranium.
- Incentives for nuclear recycling are changing due to concerns about global conflict cutting off fuel supply and the need for more clean energy.
- Technology exists to recycle nuclear waste, and it has already been demonstrated and proven.
- If we can recycle nuclear waste, it says something profound about what humans are capable of and our ability to use resources and technology to make the world a better place.
The Big Lie About Nuclear Waste - What if we could actually USE nuclear waste? - YouTube
Read also:
- Nuclear Fusion: Inside the breakthrough that could change our world | 60 Minutes (mindbrave.com)
- How Tsar bomba works! Worlds biggest nuclear bomb ever detonated (mindbrave.com)
- These Stupid Trucks are Literally Killing Us (mindbrave.com)
